Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a service that allows you to run and manage clusters of Docker containers on AWS infrastructure. It’s fully managed by Amazon. Docker Compose is a most-wanted tool used to manage containerized applications deployed on Docker. You can simply define all components in a Compose file and the run commands to manage your deployment.
The integration between Docker and Amazon ECS allows developers to use the Docker Compose CLI to create an AWS context, deploy and run multi-container Docker containers on Amazon ECS using the same commands as you do it on your local environment.
This blog post is a part of series 3 ways (EC2, ECS and AKS) to deploy Apache APISIX on AWS. In part one, we discussed the simplest way to build and run APISIX on AWS EC2 and in this walkthrough, we learn how to leverage Docker Compose to deploy containerized Apache APISIX API Gateway (together with etcd) to ECS.
Prerequisites
- ➡️ AWS account. To deploy to Amazon ECS, you need to set up an AWS account and create a IAM user if you haven't done yet follow the guide [AWS account setting-up] (docs.aws.amazon.com/polly/latest/dg/setting..).
- ➡️ Grant access permissions - Once you have AWS account, you grant access to some AWS IAM permissions as its shown on this page.
- ➡️ Docker Desktop - you need also Docker desktop installed locally to complete this tutorial. It is available for Windows or macOS. Or install the Docker ACI Integration CLI for Linux.
Throughout this blogpost, you will:
- ✔️ Get Apache APISIX example source code for Docker from GitHub.
- ✔️ Modify Docker compose file there.
- ✔️ Create an ECS context to target Amazon ECS.
- ✔️ Run APISIX on Amazon ECS.
- ✔️ Verify APISIX running.
Get Apache APISIX from GitHub
In this demo, we are using Apache APISIX Docker repo and it contains an example docker-compose.yaml file and with other config files that makes straightforward to start APISIX using docker compose. We try out this example:
Use git to clone the repository and cd into the example folder.
git clone 'https://github.com/apache/apisix-docker'
cd apisix-docker/example
Modify Docker compose file
Next, open docker-compose.yaml in a text editor. The example docker compose file defines several services: apisix-dashboard, apisix, etcd, web1, web2, prometheus, and grafana:
apisix-dashboard, apisix, etcdare the essential services required for starting apisix-dashboard, apisix, and etcd.web1, web2are sample backend services used for testing purposes. They use nginx-alpine image.prometheus, grafanaare services used for exposing metrics of the running services.
For the sake of simplicity, we are going to use and run only APISIX and etcd services in this demo. We can simply do the following changes by removing other services and defining volumes like etcd-data and apisix-data.
Let us take a look at modified docker-compose.yaml below:
version: "3"
services:
apisix:
image: apache/apisix:2.14.1-alpine
restart: always
volumes:
- apisix-data:/apisix/conf/
depends_on:
- etcd
ports:
- "9080:9080/tcp"
networks:
apisix:
etcd:
image: bitnami/etcd:3.4.15
restart: always
volumes:
- etcd_data:/bitnami/etcd
environment:
ETCD_ENABLE_V2: "true"
ALLOW_NONE_AUTHENTICATION: "yes"
ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS: "http://0.0.0.0:2379"
ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS: "http://0.0.0.0:2379"
ports:
- "2379:2379/tcp"
networks:
apisix:
networks:
apisix:
driver: bridge
volumes:
etcd_data:
external: true
name: ETCD_FILE_SYSTEM_ID
apisix-data:
external: true
name: APISIX_FILE_SYSTEM_ID
Apache APISIX has to persist etcd state and mount external configuration files like
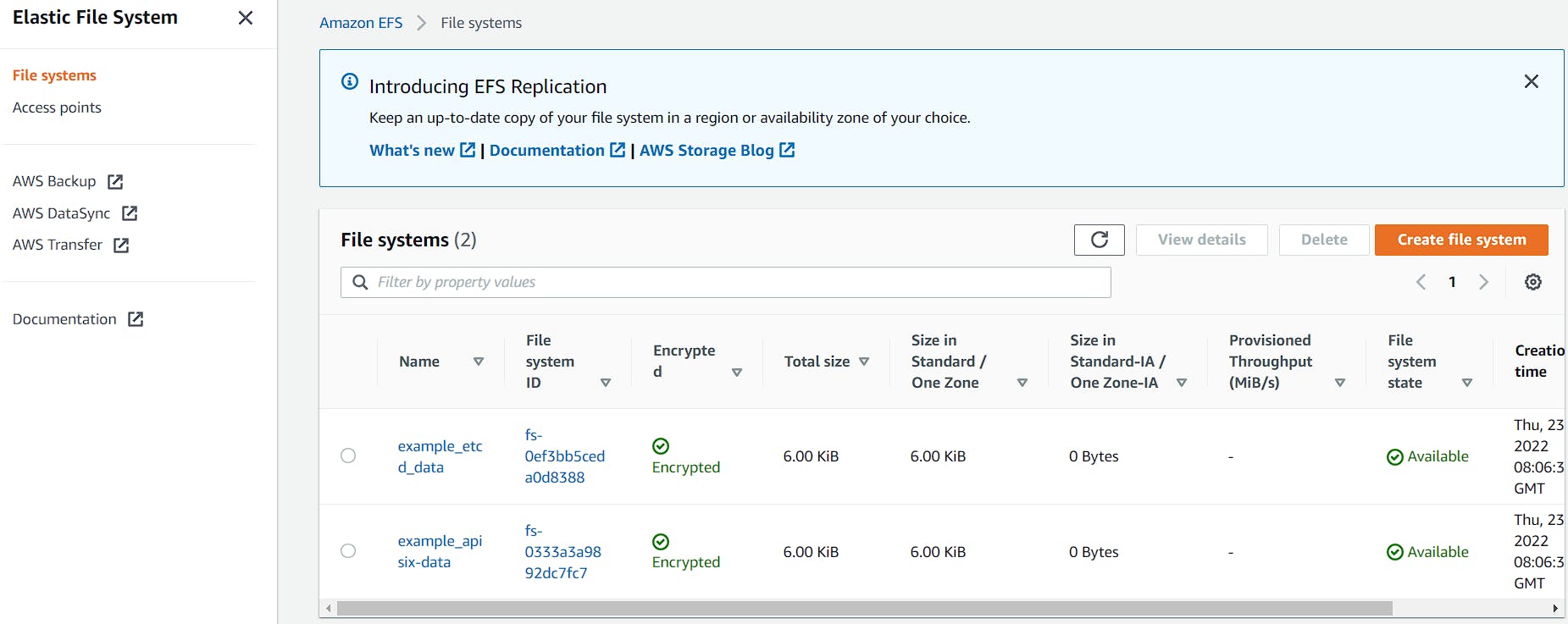
/apisix_conf/conf.yaml(defines the configs for apisix) in the repo folder onto the containers. You can store persistent data outside of the container-filesystem in Amazon Elastic File System. ECS integration supports volume management based on Amazon EFS. In the compose file to we declare volumes for existing file system where we have data stored (APISIX config files) on EFS and we use the ID/Name of the existing EFS volume. You can replaceETCD_FILE_SYSTEM_IDandAPISIX_FILE_SYSTEM_IDwith IDs of your EFS files.
If you do not specify existing EFS volume IDs, ECS integration creates automatically two new file systems in EFS:
...
volumes:
etcd_data:
apisix-data:
In this demo, I initiated manually these EFS files. For more information this tutorial (Using Amazon EFS file systems with Amazon ECS) describes the whole process very well. You can also follow the same guide to add APISIX config files to EFS.
👉
Create an ECS context to target Amazon ECS
Next, we need to create a AWS context to make Docker Compose target the Amazon ECS platform instead of pointing to the local environment which is default behavior for Docker.
To create an ECS context run the following command:
docker context create ecs apisixecscontext
Then, change to the ECS context. Subsequent Docker commands run in this context.
docker context use apisixecscontext
Run docker context ls to confirm that you added the AWS ECS context:

Run APISIX on Amazon ECS
Finally, now we can deploy APISIX with etcd to ECS by executing:
docker compose up
☝️ It takes some time to deploy ECS with other AWS services. Because under the hood, Docker Compose converts the Compose file to a CloudFormation template defining a set of AWS resources (ECS Cluster, AWS Log Group, a Load Balancer, Security Group, TargetGroup, CloudMap and etc.). Details on the resource mapping can be found in the documentation.
To check the state of the services, we can run docker compose ps command or check it directly from AWS console.
Verify APISIX running
To verify if Apache APISIX API Gateway is running in the AWS ECS, we run the below curl command and check the response from APISIX's REST Admin API. You need to replace DNS_LOAD_BALANCER to you public DNS name of the load balancer:
curl "http://{DNS_LOAD_BALANCER}:9080/apisix/admin/services/" -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1'
The response indicates that APISIX is running successfully:
{
"count":0,
"action":"get",
"node":{
"key":"/apisix/services",
"nodes":[],
"dir":true
}
}
Here we go, Apache APISIX is up and running in AWS ECS and responding to your requests 👏💪.
Troubleshoot😕
While you are deploying Apache APISIX in AWS ECS, you might get errors with mounting or accessing AWS EFS volumes like:
ResourceInitializationError: failed to invoke EFS utils commands to set up EFS volumes: stderr: b'mount.nfs4: Connection timed out' : unsuccessful EFS utils command execution; code: 32
Or
ResourceInitializationError: failed to invoke EFS utils commands to set up EFS volumes: stderr: mount.nfs4: Connection reset by peer : unsuccessful EFS utils command execution; code: 32
💁 To troubleshoot this kind of error, you can follow the guideline on the AWS knowledge center.
Recommended content
➔ Watch Video Tutorial Getting Started with Apache APISIX.
➔ Read the blog post Overview of Apache APISIX API Gateway Plugins.
➔ Read the blog post Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins.
➔ Read the blog post API Observability with Apache APISIX Plugins.
➔ Read the blog post Run Apache APISIX on Microsoft Azure Container Instance.
Community⤵️
- 🙋 Join the Apache APISIX Community
- 🐦 Follow us on Twitter
- 📝 Find us on Slack
- 📧 Mail to us with your questions.
